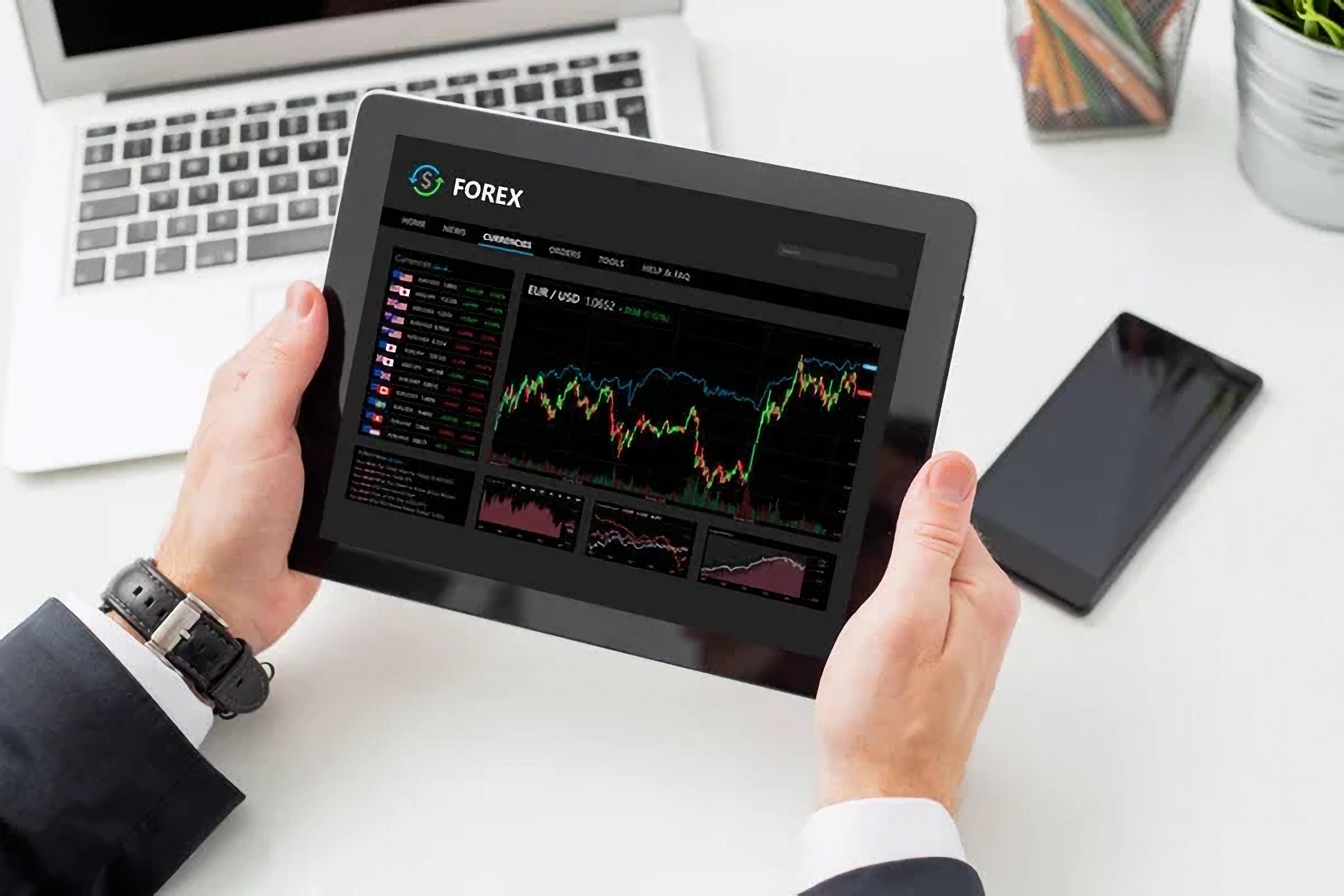
How to Read Forex Graph
In the fast-paced world of Forex trading, understanding how to read and interpret Forex graphs is crucial for success. For beginners and experienced traders alike, the ability to analyze price movements effectively can mean the difference between profit and loss. This article will provide a detailed overview of Forex graphs, including their components, types, interpretation, tools, and how to develop a successful trading strategy.
Understanding the Basics of Forex Graphs for Beginners

At its core, a Forex graph represents the historical price movements of a currency pair over a specific time frame. By visualizing price action, traders can make informed decisions based on past performance.
Key Features of Forex Graphs
- Time Frame: The duration over which price movements are plotted (e.g., minutes, hours, days).
- Price Scale: The vertical axis showing the currency pair’s price.
- Volume: Often represented below the price chart, indicating the number of transactions over a period.
Key Components of Forex Graphs: What You Need to Know

To effectively read a Forex graph, you should familiarize yourself with its key components:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Axes | The horizontal axis represents time, while the vertical axis represents price. |
| Price Action | The actual movement of the currency pair’s price over time. |
| Indicators | Tools added to the graph, such as moving averages or RSI, to help analyze trends. |
| Time Frames | Different time intervals that can be analyzed (e.g., 1-minute, 1-hour, daily). |
Understanding these components will provide the foundation needed for effective analysis.
Types of Forex Charts: Line, Bar, and Candlestick Explained

There are three primary types of Forex charts, each with its own advantages and use cases:
- Line Chart
- Description: A basic representation that connects closing prices over a specific period.
- Advantages: Easy to read, ideal for beginners.
- Disadvantages: Lacks depth; does not provide information about opening or high/low prices.
- Bar Chart
- Description: Displays the open, high, low, and close prices (OHLC) for each time period.
- Advantages: Offers more information than a line chart.
- Disadvantages: Can be confusing for beginners due to multiple components.
- Candlestick Chart
- Description: Similar to bar charts but uses colored “candlesticks” to represent the price action.
- Advantages: Visually appealing and provides immediate insight into market sentiment.
- Disadvantages: Requires some understanding of candlestick patterns for effective interpretation.
In summary, while line charts provide simplicity, candlestick charts offer the most detailed insights into market behavior.
Interpreting Price Movements: Trends and Patterns Unveiled

Recognizing trends and patterns in price movements is vital for successful Forex trading. Here are some key concepts:
Types of Trends
- Uptrend: Higher highs and higher lows indicate a bullish market.
- Downtrend: Lower highs and lower lows suggest a bearish market.
- Sideways Trend: Price moves within a range, indicating market indecision.
Common Patterns
- Head and Shoulders: Indicates potential reversal from bullish to bearish.
- Double Top/Bottom: Suggests potential price reversals after a trend.
By identifying these trends and patterns, traders can make more informed decisions about when to enter or exit a trade.
Tools and Indicators for Effective Forex Chart Analysis
To enhance your analysis, consider using the following tools and indicators:
- Moving Averages (MA): Helps identify trends by smoothing out price data.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): Measures momentum and can indicate overbought or oversold conditions.
- Bollinger Bands: Provides insight into price volatility and potential reversal points.
Integrating these tools into your Forex graphs can help to provide a clearer picture of market conditions.
Developing a Strategy: Using Forex Graphs for Trading Success
Creating a solid trading strategy based on your analysis of Forex graphs is essential.
Steps to Develop Your Strategy:
- Define Your Goals: Establish clear trading objectives.
- Choose Your Time Frame: Select a time frame that aligns with your trading style (day trading, swing trading, etc.).
- Analyze Charts: Regularly check Forex graphs using the techniques discussed to identify trends, patterns, and entry/exit points.
- Risk Management: Determine how much capital you are willing to risk on each trade and set stop-loss orders accordingly.
- Continuous Learning: Stay updated with market news and developments to adjust your strategy as necessary.
By following these steps and utilizing Forex graphs effectively, you can significantly enhance your trading performance.
In conclusion, mastering how to read Forex graphs is a fundamental skill for any trader. By understanding the basics, components, types, trends, and tools, you can develop a robust trading strategy that leads to success in the Forex market.



‘Volume’ was a new concept for me, but this article explained it well.
Great tips on developing a trading strategy. I feel more confident now!
‘Continuous Learning’ is key! I’m excited to keep improving my skills with this info.
‘Risk Management’ is so important! Glad you included that in the strategy section.
This article really helped me understand Forex graphs better. The explanations are clear!
‘Head and Shoulders’ pattern sounds complex, but the explanation made it clear!
I appreciate the breakdown of different chart types. It makes it easier for beginners like me.
The section on trends is very useful! I now know what to look for in my trades.
Candlestick charts seem interesting! I will try using them in my next trades.
This guide on reading Forex graphs is perfect for beginners. Thanks for sharing!